
- #Adobe audition podcast workflow how to#
- #Adobe audition podcast workflow manual#
- #Adobe audition podcast workflow professional#
But it doesn’t only stop at basic podcast editing. Together, these two features empower creators to produce studio-quality audio content more efficiently.
#Adobe audition podcast workflow professional#
You can make your recordings sound like they were recorded in a professional studio with a single click.
Studio Sound boosts audio recording quality, especially in noisy or non-ideal environments. That means you can fix small errors in a podcast or voiceover without having to re-record it. Overdub lets you make new voice recordings from text using a synthetic version of your own voice (or, alternatively, a stock voice). With Descript, you also get access to two incredibly popular AI features: Overdub and Studio Sound. Descript also offers non-destructive editing, allowing you to make changes without altering the original audio file. Unlike traditional editors that rely on waveforms, Descript allows you to edit the transcribed text, and the corresponding video or audio file gets updated automatically. Selecting a region changes the language and/or content on of Descript's standout features is its transcription-based editing. Note: To use the Export with Adobe Media Encoder, you must have installed the same version of Adobe Media Encoder as Audition on your computer. When it comes to efficient compression, smaller file size, and better audio quality, a 64-kbps AAC-HE (high efficiency) stereo file would fare better than a 128-kbps MP3.Īudition gives you a range of output and encoding options within the application or outside, such as exporting to Adobe Media Encoder.Īdobe Media Encoder includes a series of formats and presets that allow you to render and publish high-quality audio output from Audition. For mono, podcast talks, 64-kbps MP3 is used. For stereo podcasts, 128-kbps MP3 is widely used. Recording your podcast at a higher encoding rate retains rich audio details. AAC also supports metadata that MP3 does not support, such as Chapter Markers, and embedded links and images. m4a files, offer better audio quality at smaller file sizes compared to MP3. MP3 is the most popular format used by podcasters. 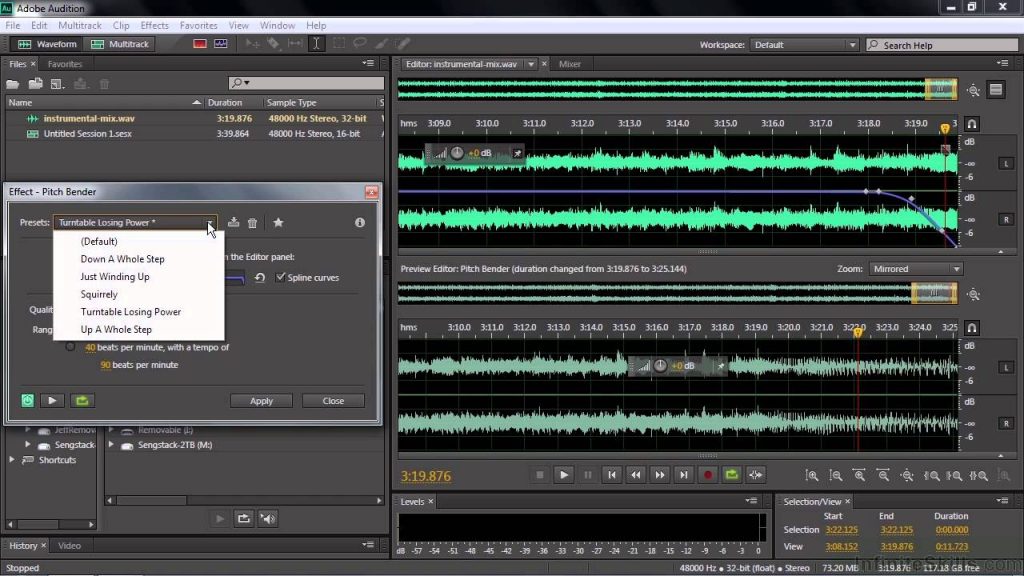
The most common formats for podcast delivery are MP3 or AAC. Importing video and working with video clipsĪfter you are done with your edits and previewing your changes, you can save your podcast in the format and settings that suits your target media.
#Adobe audition podcast workflow how to#
How to match, fade, and mix clip volume with Audition. 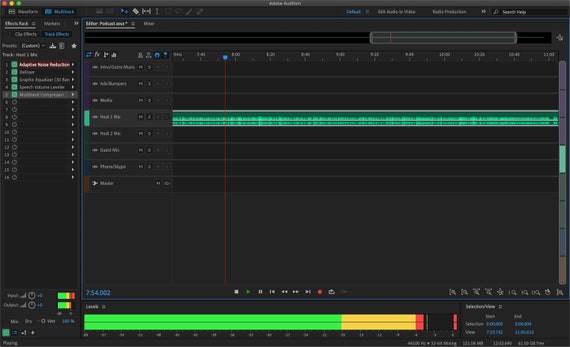 Arrange and edit multitrack clips with Audition. How to use special effects with Audition. Diagnostics effects (Waveform Editor only) for Audition. Apply amplitude and compression effects to audio. Doppler Shifter effect (Waveform Editor only).
Arrange and edit multitrack clips with Audition. How to use special effects with Audition. Diagnostics effects (Waveform Editor only) for Audition. Apply amplitude and compression effects to audio. Doppler Shifter effect (Waveform Editor only). #Adobe audition podcast workflow manual#
Manual Pitch Correction effect (Waveform Editor only). Fade and Gain Envelope effects (Waveform Editor only). Applying effects in the Waveform Editor. Analyze phase, frequency, and amplitude with Audition. How to automate common tasks in Audition. Inverting, reversing, and silencing audio. How to copy, cut, paste, and delete audio in Audition. Displaying audio in the Waveform Editor. Matching loudness across multiple audio files. Session Markers and Clip Marker for Multitrack. 
Edit, repair, and improve audio using Essential Sound panel.Remove silences from your audio recordings.Monitoring recording and playback levels.Navigate time and playing audio in Adobe Audition.Create, open, or import files in Adobe Audition.Customizing and saving application settings.Connecting to audio hardware in Audition.Applying effects in the Multitrack Editor.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
